3 Pillars of Search Engine Optimization
3 Pillars of SEO: How to Get Found on Search
Search engine optimization, otherwise known as SEO, drives traffic to your website, enhances user experience, and is instrumental in generating qualified leads, all by obtaining search engine result prominence. While this strategy is in constant flux, there are three pillars of SEO that create the foundation of any well-considered effort to boost brand visibility and improve search rankings: technology, on-page, and off-page. Search engines like Google will scan your content and links to assess the level of discovery, relevance, and authority associated with your site. Let’s discuss a few ways you can leverage these three pillars into search engine optimization domination!
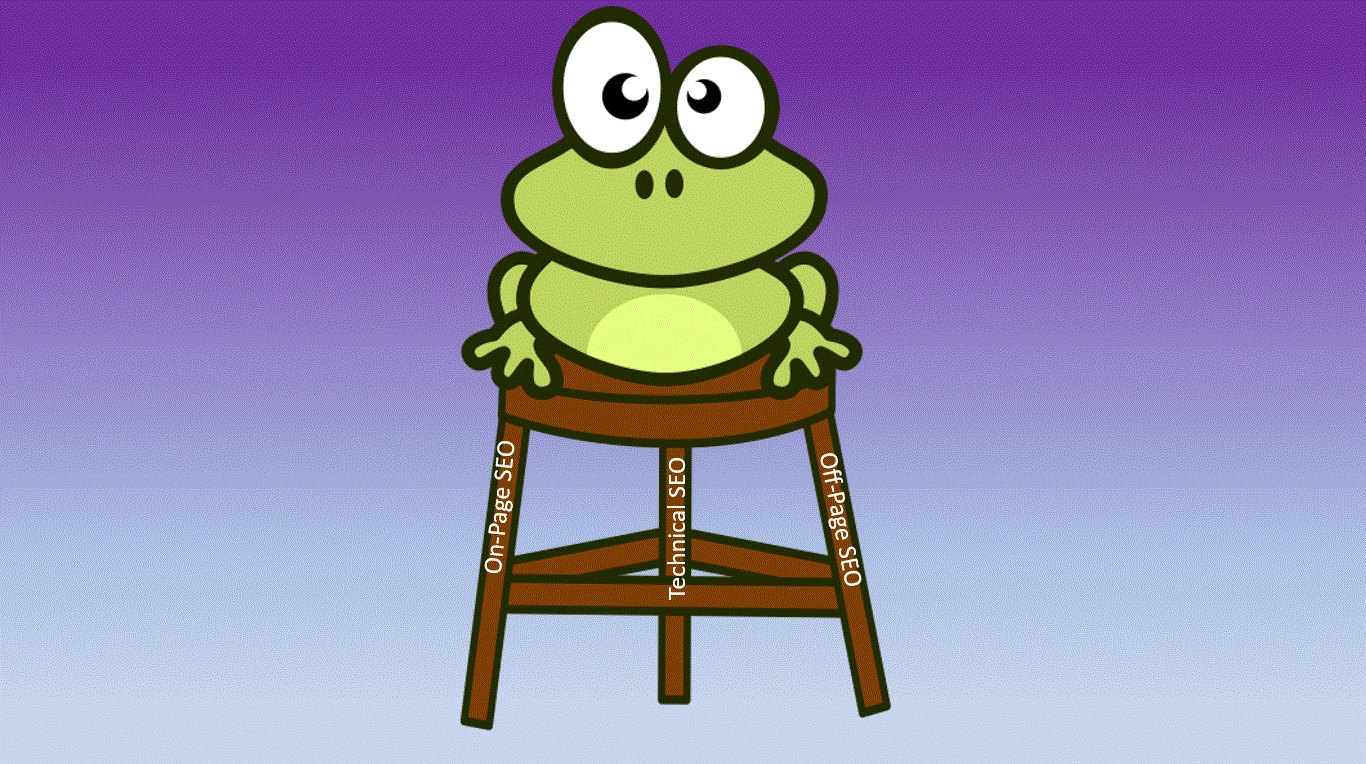
Technical SEO
Your site’s technical features and abilities are the first indicators of quality, and the first pillar of a strong SEO optimization strategy. Technical abilities encompass any element or solution used to increase customer satisfaction and ease of use for your site. Using technology, there are countless ways to drive traffic to your site, increase lead generation, and thus, satisfy customers.
Site Speed
How fast your site loads is a major indicator of the quality of your site and chosen content. Statistically, websites with a load time of 2 seconds have an average bounce rate of 9%. A marginal increase in load-time, from 2 seconds to 5 seconds, sees the bounce rate rise to 38%! Google will take note of a high bounce rate, and will adjust your ranking accordingly, so it really matters how fast your site loads! To ensure you make the cut, consider deployment of load-time reducing technology like compression, redirect reduction, browser caching leveraging and using a professional content distribution network.
Mobile-Friendliness
 Mobile phones have overtaken PCs as the device of choice for internet access, browsing and even online shopping. Mobile phones, in a myriad of styles and formats, have become a one-stop-shop for all things internet, causing potential customers to puzzle over why your text, products, screens and buttons are cut off, or extend beyond the edges of the device. It’s incredibly critical that you SEO optimize your website for easy mobile phone and device viewing and use, to avoid forcing customers to seek out a new device to view your content, or more likely, a different mobile-friendly business site.
Mobile phones have overtaken PCs as the device of choice for internet access, browsing and even online shopping. Mobile phones, in a myriad of styles and formats, have become a one-stop-shop for all things internet, causing potential customers to puzzle over why your text, products, screens and buttons are cut off, or extend beyond the edges of the device. It’s incredibly critical that you SEO optimize your website for easy mobile phone and device viewing and use, to avoid forcing customers to seek out a new device to view your content, or more likely, a different mobile-friendly business site.
User Experience
At the heart of SEO optimization strategy is user experience (UX). While SEO prioritizes search engines, your UX targets your website users and customers. These two elements should work in concert to ensure that every visit to your site is easy, intuitive and transparent. Did you know that 52% of users say they will abandon a site due to something as seemingly simple as aesthetics? Users know what they want, and are spoiled for choice – making your focus on creating an excellent user experience, of critical importance.
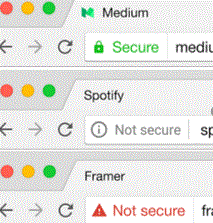
HTTPS: Secure site
The cyber threat landscape, awash with ransomware, malware and viruses, has forced a significant shift in the way we prioritize our data privacy, and our expectations of companies who we trust with our information. Using an “HTTPS” site and purchasing an SSL certificate, signals to search engines and customers that your site is safe to interact with, and that you can be trusted with their vital personal or financial information. Your decision to prioritize site security can also be used in your SEO strategy and marketing material, serving as an organic draw for network-security-conscious users.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO encompasses everything users see and interact with on your page. Search engines prioritize well-constructed websites, with clear and original content, but this content can’t be created randomly. There are a few strategies you can use for your on-page content to ensure it is top-rung and at the top of the search engine results.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the SEO process of discovering the most commonly used keywords, when users are seeking out information via search engines, and incorporating those keywords into your original content. Search engines scan for applicable keywords within your content, moving more artfully and keyword-optimized sites to the top of the search page. Thorough keyword research can be a valuable source of useful queries, data and ranking difficulty, elements proven to attract the attention of search engines, and users alike.
Understanding Search Intent
Understanding ‘search intent’ is determining what keywords users are turning too, and what their overall intention is. Most searches are performed by users seeking out information on general products and services, not your particular company or site. Start your search engine optimization strategy by incorporating broad search terms into your content, and bare down into more specific phrases and keyword variations. Finally, cap off your content with specifics about your product or service features, explaining why and how your product or service meets user needs.
Content Strategy
A good content strategy is the process of regularly creating unique content, targeted at meeting business goals and customer needs. For example, if one business goal is to drive more traffic to your mobile site, focus on creating content and links that promote awareness of your targeted site. If your focus is on the success of a new product or service, use your SEO content to draw reader interest and inform them about your offerings.
Internal Linking
Creating internal links between your content is a great way to drive traffic from one page of your site, to the next. Both users and search engines scan for links to relevant and reputable content. Once your content has captured Google’s attention using internal links, customers can use these same links to navigate your page, products and other content. A great content strategy comes in here, as content should always be complementary, informative and should help drive sales leads by giving customers new ideas and product options.

Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to any user or company activity outside your website, aimed at building search rankings on search engines. Link building with outside links is an easy association to draw, but off-page SEO is considerably more complex. Good examples of off-page SEO include posting as a guest on an outside blog with internal linking to your page, or even submitting personal comments on another post or article.
Backlinks
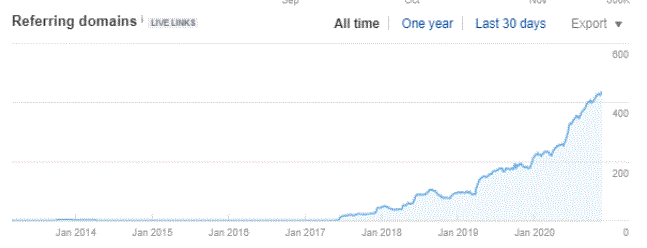
Backlinks are also referred to as inbound or incoming links. While forward-thinking business owners are creating links to outside sites and content to boost their search engine results, other businesses will be seeking you out in hopes of doing the same. Backlinks from other sites are a beacon of confidence, and show your users and customers that your content is safe, informative and helpful to others – one of the most ringing endorsements your site can get. Your SEO content strategy will also play an important role here, as unique and original content is significantly more likely to attract traffic, over slip-shot, irrelevant backlinks that are bought, not earned.
Local SEO
Incorporating local SEO into your search engine optimization strategy is proven to attract loyal local customers to your business. Almost half of all Google searchers have a ‘local intent,” meaning customers are seeking out businesses close to their physical location. Many businesses are taking advantage of technology to leverage local SEO, into long-term success, using paid software or even open-source options like Google My Business, a free tool for organizations to manage their online presence. Local customers love tools like this, as it allows you to edit and verify your business information, an element customers consider a good and transparent business strategy.
Search engine optimization is a complex and ever-changing process, requiring a great deal of time and focus to learn and use effectively. Luckily, with little effort and a few Google searches, you can discover anything you need to know about the three pillars of SEO, and how they can enable a future-proof and successful business. For more information about top-to-bottom, successful SEO strategies, contact Apogee Results today!
Want in-sight into your SEO strategy?
Fill out the form below to request a complementary evaluation of your digital marketing today.



















 Lena Schulz is Apogee’s newest Social Media and PPC Full Time Intern. She graduated from Loyola University Maryland with a degree in International Studies and Marketing. She assists our team by providing clients with community social media management, PPC strategy and content writing. In her free time, she loves to work on graphic design, discover new foods and relax by the nearest body of water.
Lena Schulz is Apogee’s newest Social Media and PPC Full Time Intern. She graduated from Loyola University Maryland with a degree in International Studies and Marketing. She assists our team by providing clients with community social media management, PPC strategy and content writing. In her free time, she loves to work on graphic design, discover new foods and relax by the nearest body of water.


